Auto-Clustering
Auto-Clustering of Instances via Topology Wizard
The platform provides an on-demand automatic clusterization for some of the managed templates. Such automation significantly simplifies and speeds up the creation of a reliable production-ready cluster for your project.
Below, we’ll consider the following points:
-
supported stacks (with clusterization specifics)
-
auto-clustering management
-
cloud scripting usage
Templates with Supported Auto-Clustering
Currently, the following templates support the newly added clustering feature (with even more stacks to be added in the future):
-
application servers - Tomcat/TomEE, GlassFish, Payara, Jenkins, WildFly
-
SQL databases - MySQL, MariaDB, Percona, PostgreSQL
-
NoSQL database - Couchbase, MongoDB, Redis, OpenSearch
-
storage server - Shared Storage Container
Tip: Your particular service hosting provider can configure and implement auto-clustering for some additional stacks, which are not defined in the list.
Tomcat/TomEE
A highly available Tomcat/TomEE cluster that can balance the load across compute nodes to enhance performance and resilience. The implementation provides session replication, context attribute replication, and cluster-wide WAR file deployment.
Note: The Auto-Clustering feature for Tomcat and TomEE is available since the following stack versions:
- Tomcat - 10.0.5; 9.0.45; 8.5.64; 7.0.108
- TomEE - 9.0.0-M3; 8.0.5
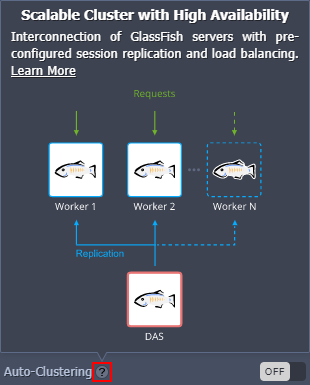
GlassFish
Interconnection of the GlassFish servers with pre-configured session replication and load balancing.
Payara
Interconnection of the Payara servers with pre-configured session replication and load balancing.
Jenkins
A master Jenkins node in the master-slave mode with auto-scalable Java Engine workers and pre-installed plugins to support building and deployment automation for organizing continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) pipelines.
WildFly
WildFly nodes in Domain Mode with enabled clustering to get high availability and guarantee the continuous performance of a deployed Java EE application.
MySQL
Auto-Clustering is provided for the 5.7.x and 8.x MySQL versions only.
Automatic clusterization of the databases with pre-configured replication and auto-discovery of the nodes.
Based on your requirements, you can select Scheme of the following types:
- Primary-Primary with Extra Secondaries Pre-configured replication with two interconnected primary databases. During the horizontal scaling, the cluster is extended with additional secondary nodes.
- Primary-Secondary with Extra Secondaries Pre-configured replication with one primary and one secondary database. During the horizontal scaling, the cluster is extended with additional secondary nodes.
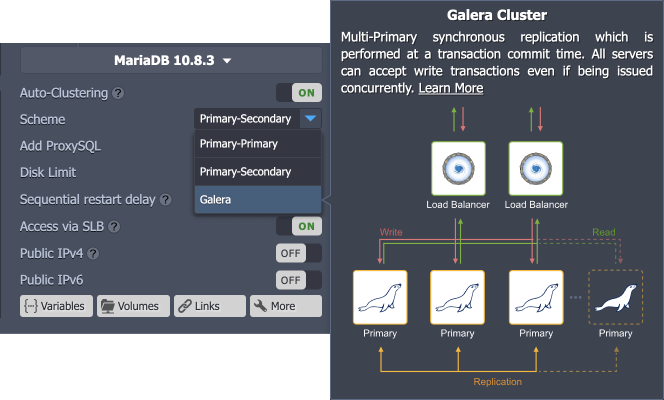
MariaDB
Auto-Clustering is provided for the 10.x MariaDB versions only.
Automatic clusterization of the databases with pre-configured replication and auto-discovery of the nodes.
Based on your requirements, you can select Scheme of the following types:
- Primary-Primary with Extra Secondaries Pre-configured replication with two interconnected primary databases. During the horizontal scaling, the cluster is extended with additional secondary nodes.
- Primary-Secondary with Extra Secondaries Pre-configured replication with one primary and one secondary database. During the horizontal scaling, the cluster is extended with additional secondary nodes.
- Galera Cluster All servers can accept updates even if being issued concurrently.
Percona
Automatic clusterization of the databases with pre-configured replication and auto-discovery of the nodes.
Based on your requirements, you can select Scheme of the following types:
-
Primary-Primary with Extra Secondaries Pre-configured replication with two interconnected primary databases. During the horizontal scaling, the cluster is extended with additional secondary nodes.
-
Primary-Secondary with Extra Secondaries Pre-configured replication with one primary and one secondary database. During the horizontal scaling, the cluster is extended with additional secondary nodes.
- XtraDB Cluster A database clustering solution that ensures high availability, prevents downtime and data loss, and provides linear scalability for a growing environment.
PostgreSQL
Pre-configured PostgreSQL database cluster with asynchronous primary-secondary replication and automatic addition of the new nodes into the cluster (as secondaries).
Couchbase
Automatically interconnected Couchbase servers with the pre-configured auto-scaling and rebalancing to provide a single highly available data storing system.
MongoDB
Automatic configuration of a highly-available and reliable MongoDB replica set with auto-discovery of the new nodes.
Redis
Automatization for a distributed implementation of Redis Cluster - an open-source, in-memory data structure store. It is usually used for caching, data storing, as a message broker, and for other tasks. The provided topology consists of at least three Primary servers, each with a Secondary node to ensure the read load distribution and auto-recovery if the Primary goes down.
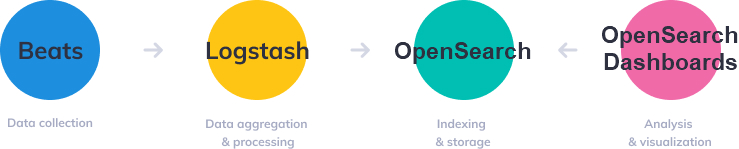
OpenSearch
Automatic clusterization of a community-driven, open-source search engine that provides a distributed, multitenant-capable full-text search. Solution provides built-in settings to add the OpenSearch Dashboards for data visualization and Logstash for processing logs.
Shared Storage Container
Automatically configured, reliable storage cluster (replicated volume) based on the Gluster solution, which ensures data safety. In case of failure of one or several nodes, the AutoFS client automatically switches to the working instances, providing storage high-availability.
Auto-Clustering Management
- The Auto-Clustering feature can be enabled for the node group through the same-named switcher in the central part of the topology wizard (if available for the selected stack).

Tip: Based on the specific implementation, the Auto-Clustering option can be:
- mandatory enabled (e.g. for the Couchbase database)
- provided with some additional settings (e.g. cluster scheme and ProxySQL load balancer for the MySQL database)
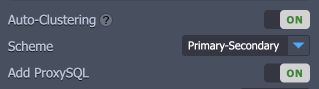
- restricted by the minimum/maximum nodes count and/or scaling mode (e.g for the MariaDB Galera type)
- Herewith, to get additional information on the cluster to be created, you can hover over the question mark next to the switcher. Within the appropriate pop-up frame, you can find a short description, which is usually supplemented with a topology scheme and a link to the more detailed overview.
Tip: Additional info on the various database cluster types can be viewed by hovering over the appropriate Scheme:
- The other settings can be configured just as for any regular environment.
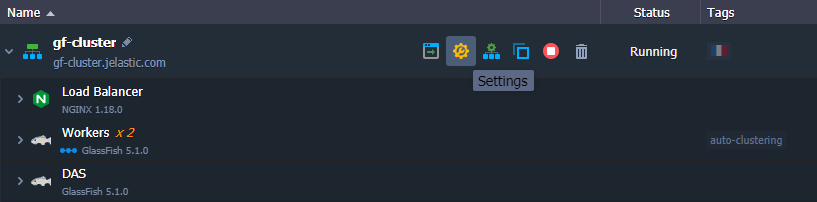
Note: After being configured, auto-clustering cannot be disabled from the topology wizard.
- If needed, you can track the cluster configuration logs via the platform console:
https://app.{platformDomain}/console
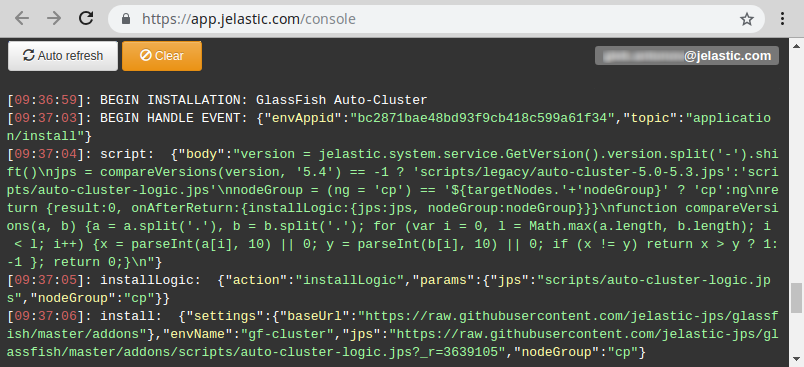
For example, you can use this info for debugging while developing packaged solutions with Cloud Scripting, which utilize the auto-clustering feature.
Setting Up Auto-Clusterization with Cloud Scripting
In order to define auto-clustering settings in your JPS solutions, a new cluster property can be used. For example:
- Enable or disable auto-clustering for the specific layer.
"nodeGroup": "couchbase", "cluster": true | false
- Additional parameters for auto-clustering can be provided in the following way (for example, can be required to select a database cluster scheme):
"nodeGroup": "mysql", "cluster": { "scheme": "master" }
- If needed, the default JPS manifest with the clusterization steps can be substituted with a custom one:
"nodeGroup": "mysql", "cluster": { "jps": "http://.../custom-manifest.jps", "settings": { "scheme": "master" } }
- Based on the particular cluster requirements, some topology restrictions may be needed (e.g. the minimum/maximum number of nodes, scaling mode, etc.). It is implemented through the validation property.
Herewith, this parameter can be specified for any JPS package, e.g. check the YAML example below:
type: install name: Validation nodes: image: alpine nodeGroup: cp count: 2 validation: minCount: 2 maxCount: 3 scalingMode: stateful
That’s it! Now, you can easily use the auto-clustering solutions supported by the platform, as well as all benefit from the implementation specifics.